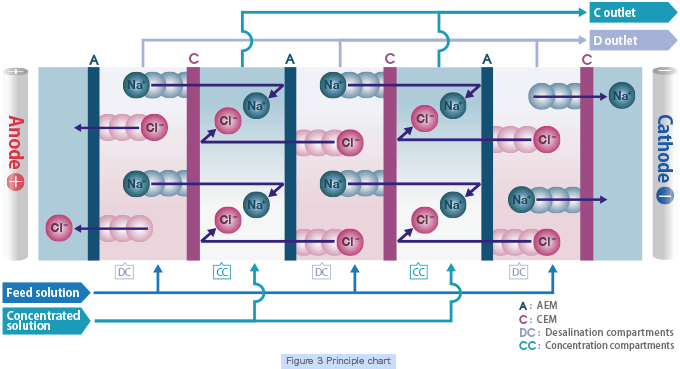
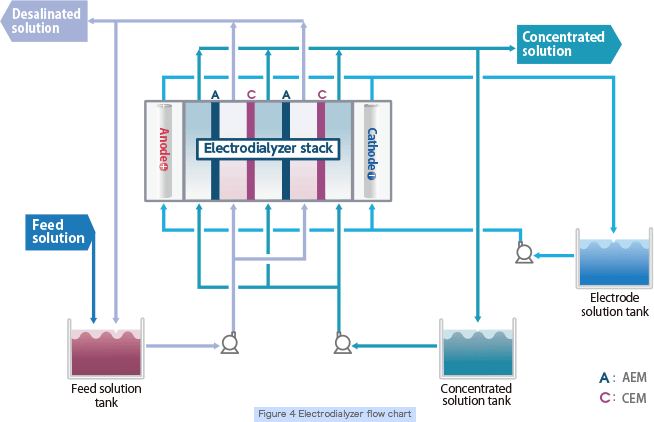
Electrodialysis is a separation technology utilizing electrophoresis of ionic substances in solutions and the selective permeability of ion exchange membranes to separate ionic substances in aqueous solution, enabling efficient desalination, concentration, refining and recovery. There are two types of ion exchange membranes. Cation exchange membrane selectively allows cation permeation and anion exchange membrane selectively allows anion permeation. In an electrodialyzer, a large number of these membranes are arranged alternately between two electrodes and direct current is applied to separate ions in solution (Figure 3).



Desalinates, concentrates, refines and recovers ionic substances.
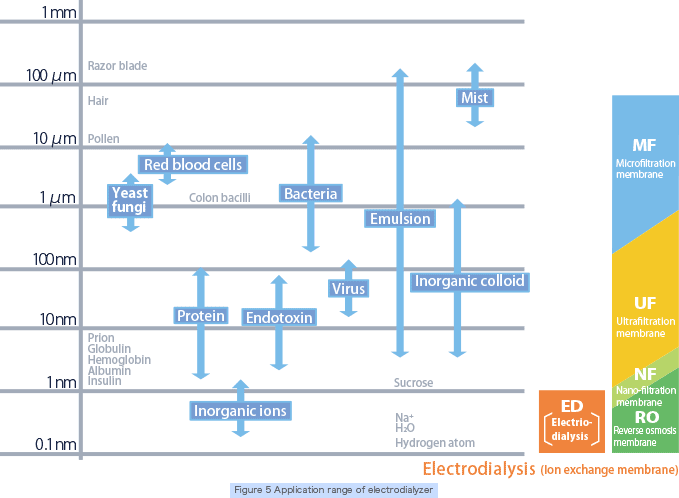
Selectively separates ionic substances.
Removes ionic substances from non-ionic valuables.
 |
Requires no heating or pressurization which keeps components consistent. |

The rates of desalination and concentration can be controlled.
 |
No regeneration required and continuous operation for an extended period of time is possible. |
 |
Electrodialyzer produces a low noise and low vibration compared with RO and also features ease of handling. |


・Salt production from seawater
・Desalination of soy sauce
・Desalination of oligosaccharide
・Desalination/concentration of leachate from a landfill
・Desalination/concentration of processing waste solution
・Acid recovery of aluminum sash pickling process
・Recovery of alkali waste solution


![Electrodialyzers[ACILYZER ED]](images/03_title.jpg)


