HOME >
Products > Bipolar Membrane Electrodialyzer [ACILYZER BPED products]
A bipolar membrane is an ion exchange membrane composed of an anion exchange layer and a cation exchange layer (Figure 10).
Applying bipolar membrane with DC current, water is split inside the membrane and then proton (H+) and hydroxyl ion (OH-) are generated. This unique function of water splitting is utilized for production of an acid and a base from a corresponding salt in combination with conventional monopolar ion exchange membrane.


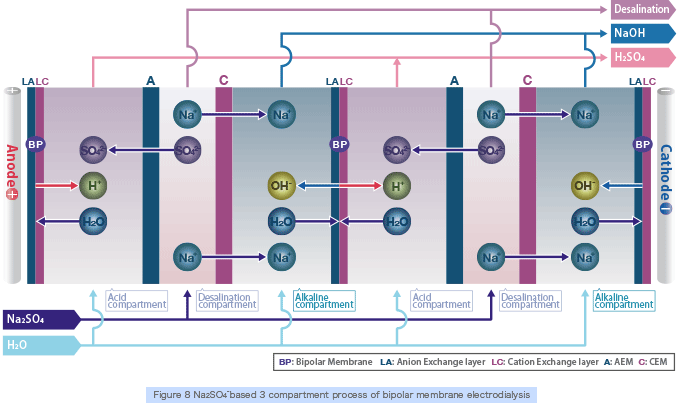
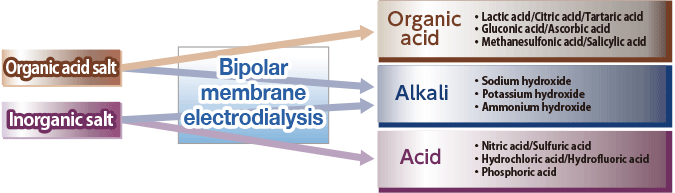
By supplying inorganic salt (e.g., Na2 SO4) to the 3 compartment process bipolar membrane electrodialysis stack (Figure 8), which combines anion, cation and bipolar membranes, the anion (SO42-) will permeate through the anion exchange membrane and combine with the H+ ion which is split at the bipolar membrane to produce acid (H2SO4). On the other hand, the cation (Na+) will permeate through the cation exchange membrane and combine with the OH- ion which is split at the bipolar membrane to produce alkali (NaOH) (the opposite reaction of neutralization will occur).
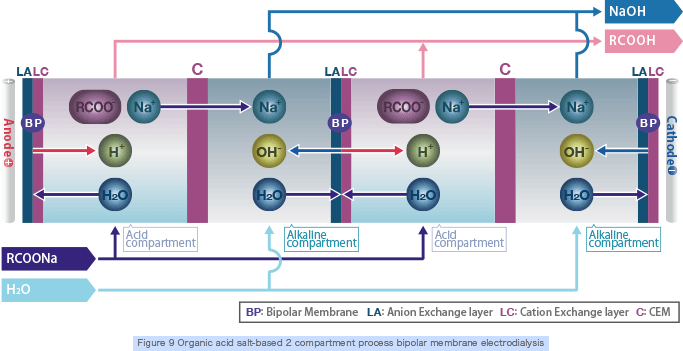
Organic acids and alkali are produced by supplying organic acid salt (weak acid salt) into the 2 compartment bipolar electrodialyzer stack (Figure 9) that is made of bipolar membranes and cation exchange membranes combined together.


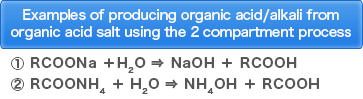
・Production of organic acid from organic acid salt
・Production of amino acid from amino acid salt
・Production of acid and alkali from waste solution with salt
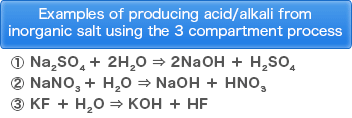
・Production of acid and alkali from inorganic salt


![Bipolar Membrane Electrodialyzer [ACILYZER BPED products]](images/05_title.jpg)